Ketosis treatment advice
The ketosis treatment advice decision support module aims to identify cows potentially suffering from ketosis and recommends a health intervention. Click on the advice to see the deviating parameters that explain why this cow is suspected of ketosis and use this information to help you decide whether to apply a treatment plan or not.
Why the ketosis treatment advice?
Research has shown that the average ketosis incidence in a herd is around 11-49%, and not everyone is aware of the ketosis incidence in their herd. It is important to detect and treat cows with ketosis because it can lead to a variety of health complications such as reduced milk yield, weight loss, increased risk for postpartum diseases, displaced abomasum, metritis, and poor fertility. Consequently, the compounding cost of these health issues have a significant financial impact when considered at herd level.
We aim to bring suspected ketosis cases under attention to prevent cows from becoming too sick and to save time and money.
The ketosis treatment advice model
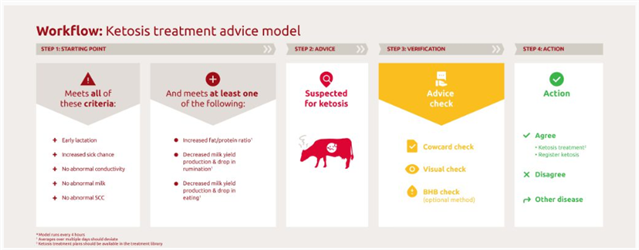
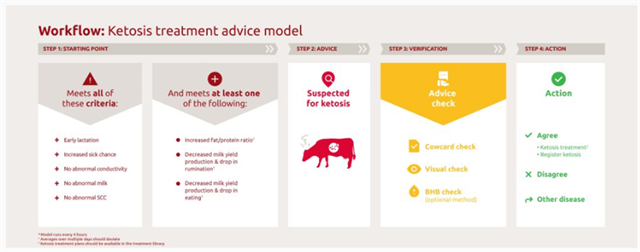
In between signaling the first symptoms of ketosis to taking the final decision, there are several steps that need to be considered. This ketosis treatment advice model will help you find animals at risk of developing ketosis and memorize what actions to consider before deciding to treat the cow and if so, what treatment is applicable.
When is advice given?
In order to receive the advice, Horizon needs to be connected to the internet and in case you are a new customer, it needs to be running for at least 2 days.
Not all cows are able to receive a ketosis treatment advice. Firstly the cow should meet all of these criteria:
- The cow is in early lactation (between lactation day 5 and 60)
- Increased sick chance (>10)
- No abnormal conductivity (<95)
- No abnormal milk, e.g. blood, colostrum, water or any other abnormality
- Somatic cell count is less than 500In the last 7 days no ketosis treatment is added or ketosis treatment advice is accepted or disagreed
Additionally, the cow should meet two or more of the following conditions:
- Increased fat/protein ratio of >1.3 over 5 days*
- Milk yield is lower than predicted milk yield
- Drop in eating time
- Drop in rumination time
*If you have a mixed herd and all breeds are milked at the same location, the fat/protein ratio might be less reliable due to averaging of the fat and protein results. As a result, the ketosis advice might be less reliable for mixed herds.
Please note that cows with some advice are not shown on the health report, reason being the health report refreshes every few minutes and the ketosis advice is generated every 4 hours. If sick change drops, the cow will fall off the health report, but the advice will stay until the next calculation.
The severity of ketosis is calculated depending on how much the health parameters deviate. For cows with severe or mild symptoms, we propose a treatment from your treatment library, e.g. Catosal. If the cow is at risk, we propose fixed feeding. The latter option is only available if you have a Titania. Depending on the severity, the last selected treatment will be used for the next advice. It is very important to set your treatment plans in conjunction with your veterinarian.
Currently, the advice provided is there to support you in your farm management and can be used alongside your own observations. Currently, we catch around 80% of all ketosis cases at a farm. The main reason for this is because we only have information available from indirect parameters. Cows with deviating health-related parameters are shown in the health report; if the data indicates that she shows ketosis symptoms, a ketosis treatment advice is generated. If parameters do not deviate sufficiently, no advice is generated.
There is a difference between identifying cows with ketosis based on measuring ketone bodies (BHB) in bodily fluids and detecting ketosis based on the ketosis treatment advice in Horizon. This has to do with the definition of ketosis; do you identify ketosis based on a BHB value above a certain threshold, or is ketosis a state in which the cow is unable to cope with the negative energy balance? For the advice the second definition is used. This means that if you measure a cow and she has an increased BHB concentration in bodily fluids, she might not have a ketosis treatment advice in Horizon. The reason for this is that not all cows with increased BHB show ketosis symptoms at the moment of sampling (such as rumination drop, decreased milk yield and/or increased fat-protein ratio). This likely indicates that these cows are able to deal with the negative energy balance without treatment. Additionally, BHB values can fluctuate over the course of the day, the ketosis treatment advice is based on a deviation over a time period.
Responding to advice will help us improve accuracy in the future. Additionally, if you enter BHB blood test results via the advice screen or Scores via the plus button, they will help us improve the ketosis model.
Learn here how to respond to a ketosis treatment advice.
How do you prevent ketosis at herd level?
When ketosis becomes a herd issue, we recommend evaluating your farm management according to the following points:
Transition management: transition is a critical point for cows due to metabolic and nutritional changes. A cow’s transition period lasts from three weeks before until three weeks after calving. Transition management of cows is critical to avoid additional pressures on the negative energy balance that cows experience after calving. Feed management: high quality feedstuffs should be fed during early lactation to meet energy and protein requirements. Evaluate rations during the dry-off period, and your rations for fresh cows. Having a feed advisor may help in setting up the right rations to meet the cows’ needs. Housing: it is important that all cows always have access to the feed fence to avoid competition. Competition is stressful, leads to uneven intervals and affects rumen health.
Applying ketosis treatment advice
A ketosis treatment alert is shown for cows showing signs of ketosis. Any deviating parameters for that cow are shown on the advice screen. Not all ketosis advice shows the same parameters; they can differ among cows. A treatment plan from your treatment library is suggested below the parameters on the advice screen.
Make sure to follow the steps in the Ketosis treatment advice workflow before applying a treatment:
How do you apply the advice?
Before using the advice, it is crucial that you register the ketosis treatment plans you use in Horizon. We recommend setting these in consultation with your veterinarian.
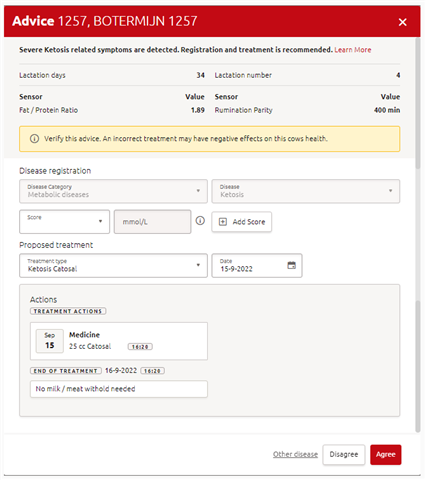
Step 1: Open the advice screen (e.g. via the health report, cowcard or advice widget)
Step 2: Check the information on the advice screen and carry out a visual check to make your decision whether to apply the action or to reject it. If you want to apply a treatment unrelated to ketosis, you can click on Other disease
Please note
1) you can only select the treatments that are registered in your treatment library.
2) It will only be possible to register fixed feeding if a Titania is installed.
3) Rumination parity means the deviation in rumination minutes compared to cows with comparable parity in the herd.
Step 3: If the cow has ketosis, select a treatment or register ketosis via the dropdown under ‘Proposed treatment’ that best suits the situation, select a date and click on Agree.
Step 3a: If you have measured BHB, you can add the BHB value and click +Add Score. This score will be saved and shown in the events page in the cowcard.
Step 4: If you disagree, click on Disagree. The advice will not return for 7 days.
