Health analysis widget
The health analysis widget is aimed to give insights into which diseases and related health treatments affect the herd with the highest incidence. The widget shows the highest five cumulative health incidences for last rolling 90 days, each compared with the average of a reference period (quarter average of the last four quarters). If hovering over the graph, it’s possible to see the number of animals treated per category.
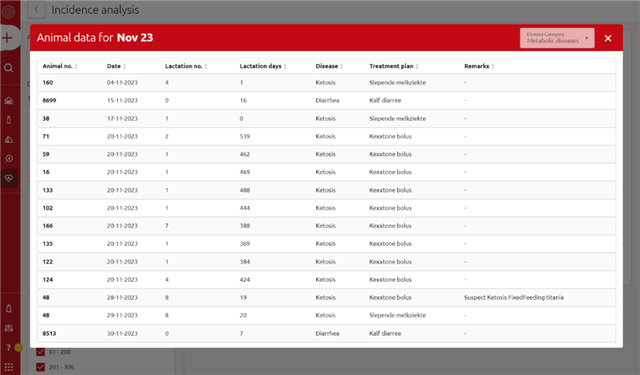
By clicking on Analyse, you will be redirected to an Analysis page where an Incidence analysis is shown
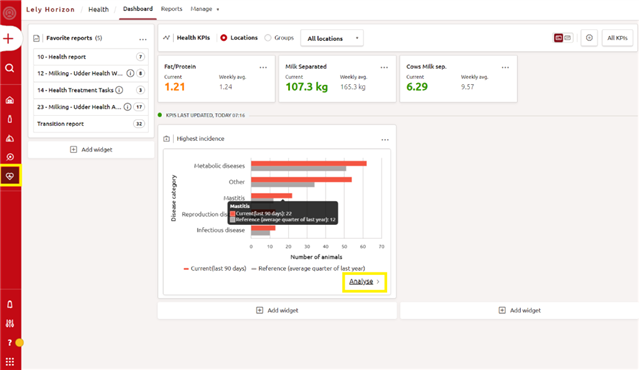
By clicking on the Split by window, you can choose which category you want to analyse in the graph (e.g. disease name or lactation stage):
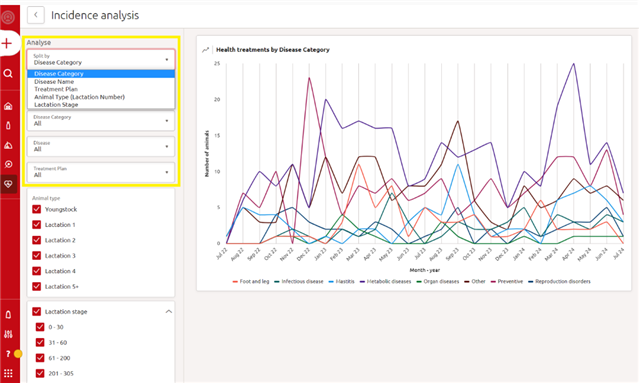
Once the health category is chosen, more filters can be added to further deep dive into the chosen category. Once all preferred filters have been selected, the graph will show the number of animals that received a certain treatment for each month during the last 24 months.
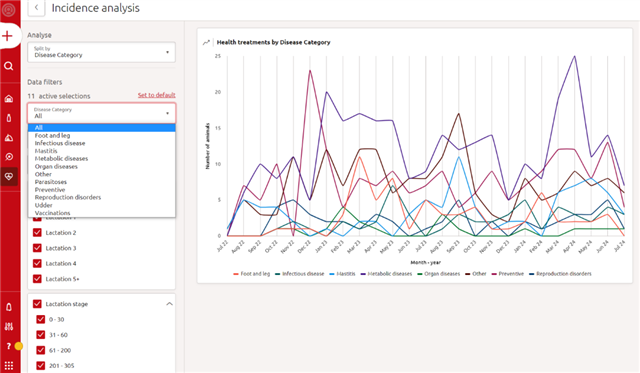
By hovering with the mouse over the datapoint for a specific month on the graph, it’s possible to see the number of animals treated for the specific disease during that month. If at one point more lines cross, then you can visualize the numbers for all of them.
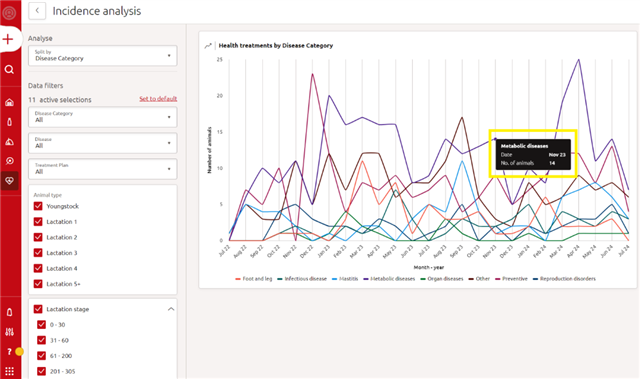
Still hovering within the graph area, the nearest datapoint will be triggered and, by just clicking, a new page will open with a complete list of all animals treated in the specific month for the specific category. In case more lines cross at the selected point, it’s possible to switch between categories on the top right corner of the window.
Medicines
Before you can create a treatment plan within Horizon, you will need to enter any medicines into the Medicines library. When entering a treatment, medicines from the library can then be chosen.
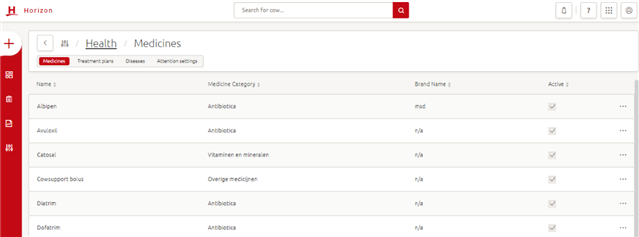
How do you create a new medicine?
Step 1: Click Manage > Health > Medicines > + > Medicine
Step 2: A new window opens where you can enter:
Medicine name. Add the medicine name as specified on the medicine label; Medicine category. Choose the correct medicine category; Brand. Write down the medicine brand; Storage days. Add the number of storage days; Meat/milk withhold. Write down the number of days or hors for meat/milk withhold; Registration code. Write down the registration code of the medicine; Treatment dosage advice. Add the dosage of the treatment and choose the type; Number of treatments. Add the number of treatments that need to be completed; Interval. Write downs the interval in days or hours; Route of administration. Choose the method of giving the medicine; Active. Choose whether the medicine is actively used or not and if this medication requires a hot rinse.
Whilst entering medicines to set up a treatment plan, it is advised to consider whether the medicine requires a ‘hot rinse’. When enabling the hot rinse option, the robot will automatically do a short main wash (includes pre-rinse, main wash with chemicals and a final rinse) after milking cows that have been treated with this medicine. Enabling the hot rinse is especially recommended for oil-based medicines that are administered intramammary.
Currently, the robot carries out an automatic default local cleaning after milking cows whose milk has been separated. This default cleaning is a one-time rinse with cold water. The default cleaning is less capable to remove oil-based medicines than a hot rinse.
Note: the default setting is ‘No’ in Lely Horizon/ T4C, as this is an extra functionality.
Note: This feature is only available for the A4 & A5 and requires at least the software set: 7.6 for the A4 and the 1.8 software set for the A5.
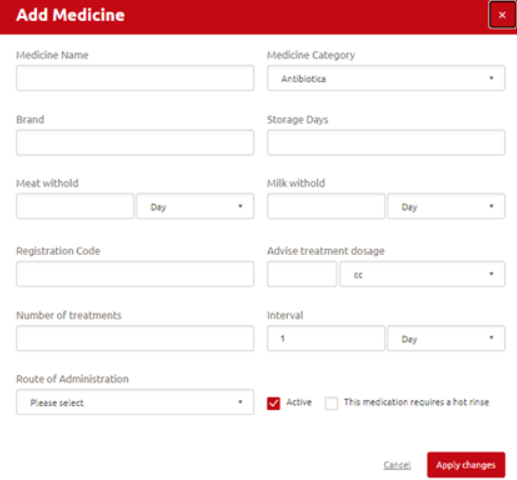
Step 3: Click Apply changes to save the changes you made
TIP!: Make sure that all information on the medicine label is entered including quantities, number of treatments per day, length of treatment in days and the period milk should be separated.
How do you edit a medicine?
Step 1: Click Manage > Health > Medicines
Step 2: Click the medicine you want to edit
Step 3: A new window opens where you can edit or delete the medicine
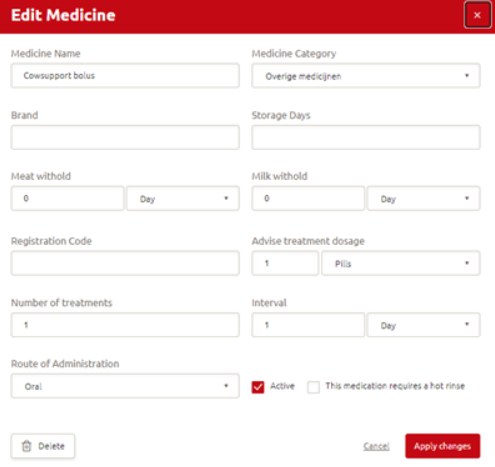
Step 4: Click Apply changes to save the changes you made
Diseases
The Disease library shows the default set of diseases that can be used in health treatment. All diseases should be found in the program, but new ones can be added if required. We recommend using the default list.
How do you create a new disease?
Step 1: Click Manage > Health > Diseases > + > Disease
Step 2: A new window opens where you can enter:
- The name of the disease;
- The correct disease category;
- The official code of the disease (ICAR code);
- The days for cure period;
- The description for this disease and if the disease is active.
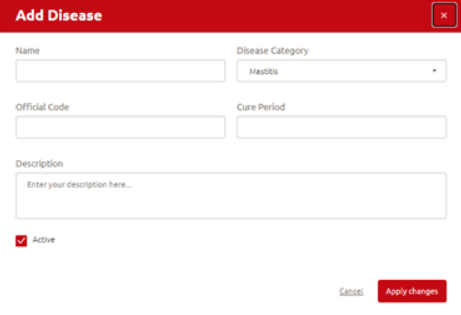
Step 3: Click Apply changes to save the changes you made
How do you edit a disease?
Step 1: Click Manage > Health > Diseases
Step 2: Click the disease you want to edit
Step 3: A new window opens where you can edit the disease or delete a disease you added. It is not possible to delete or change the default list of diseases.
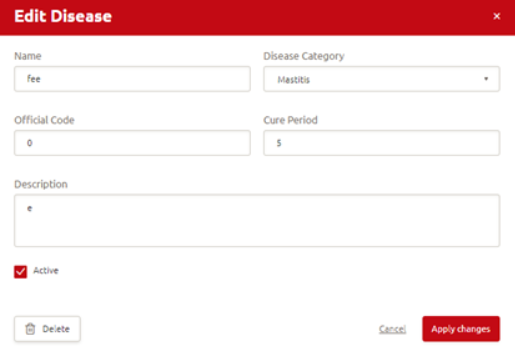
Step 4: Click Apply changes to save the changes you made
Treatment plans
Horizon keeps track of all health and medicine records. Treatment Plans can be defined to limit the time involved in entering all the information. Each plan contains a combination of diagnoses, curative health events, medication used and milk separation events and can be selected when a certain disease is entered for a cow. The main benefits of using these Treatment Plans are:
1) Treatment plans make it easier to carry out treatments, since you will be working according to established protocols. This reduces the risk of forgetting steps and increases peace of mind.
2) Treatments that need to be carried out or repeated are grouped together on the task Health treatment task for correct handling.
3) Any milk that needs to be separated is separated automatically.
4) The farmer and veterinarian have an overview of all cows that have been treated.
How do you create a new Treatment Plan?
Step 1: Click Manage > Health > Treatment plans > + > Treatment plan
Step 2: A new window opens where you can:
- Enter the name of the treatment;
- Choose if the medicine cures or prevents;
- Choose the type of disease;
- Choose the actual disease;
- Enter the advice given by the vet;
- Write your own administration in the remark and continuation blocks;
- Mark if the treatment plan is actively used or not and
- Add a medicine from the medicine list via add action.
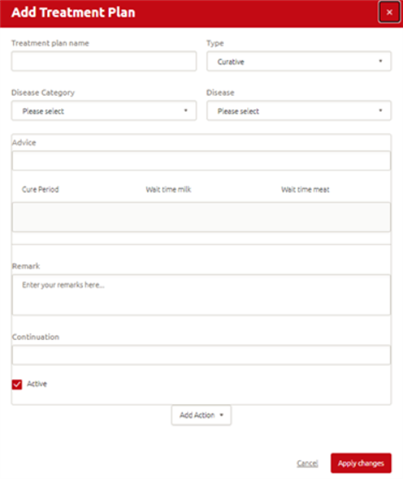
Step 3: Click ‘Apply changes’ to save the changes you made
How do you edit a treatment plan?
Step 1: Click Manage > Health > Treatment plans
Step 2: Click the treatment plan you wish to edit
Step 3: A new window opens where you can edit or delete the treatment plan
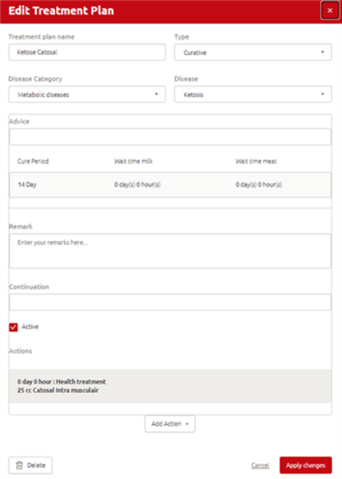
Step 4: Click Apply changes to save the changes you made
TIP!: In treatment plans, you have the option to add different medicines for different days. This means you can create easily an OV-Synch protocol for a cow and add more actions to one treatment. In addition to health treatment, you can also select:
Insemination (task depends on heat probability) Pregnancy check (task depends on reproduction check)
Hot rinse
In Lely Horizon, there is a functionality for the Lely Astronaut to clean oil-based medicines (including antibiotics): this is the ‘hot rinse’ option in the medicine library. When enabling the hot rinse option, the robot will carry out an automatic local hot rinse after milking cows treated with this medicine (when the medicine is part of a treatment plan).
What is the hot rinse functionality?
The hot rinse cleans the same parts of the robot as local cleaning (from milk cups to the three-way valves, the pre-milk device and parts of the M4Use). The hot rinse uses more capacity than local rinse. The system is first flushed with chemicals and hot water, after which the system is flushed again to ensure all chemicals are cleaned from the system. This feature is only available for the Lely Astronaut A4 and the Astronaut A5 (software set: 7.6 and above for the Astronaut A4 and 1.8 and above for the Astronaut A5).
Why the hot rinse functionality?
In the field, more and more farmers are using oil-based medicine administered intra-mammary. A hot rinse is better able to prevent oil residues from remaining in the system. The hot rinse should only be used for oil-based intra-mammary medicines, as the cleaning time increases. Oil-based components of medicines can be found in the medicine leaflet under excipients.
Note: the default setting is ‘No’ in Lely Horizon, as this is an extra functionality.
How do you use the hot rinse functionality?
A hot rinse can be activated on the medicine page. You can find the local hot rinse in the following Lely Horizon menu: Manage > Health > Medicines (add/edit), then click to open a particular medicine. The option is found at the bottom of the page. See the example in the image below.
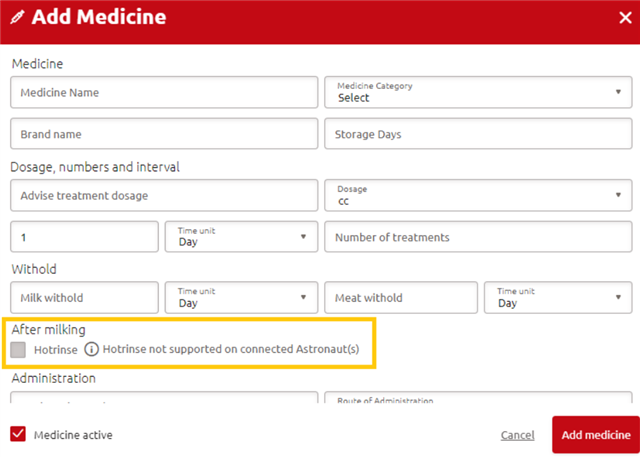
Note: existing medicines in the library stay on ‘No’ after the update. They have to be manually set to ‘Yes’ where required.
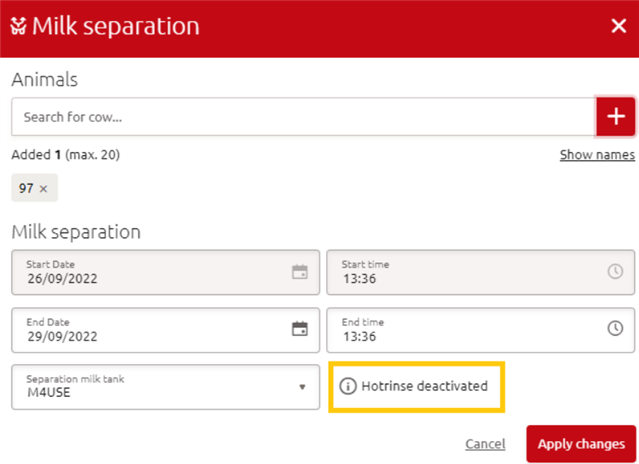
Note: the hot rinse cannot be activated with a manual milk separation.
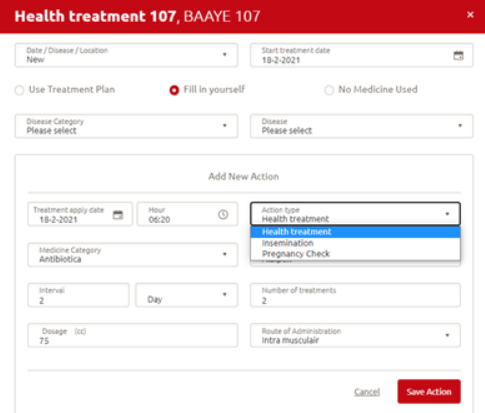
Hot rinse shown on health treatment and task
If you enter a health treatment for a cow, you can see if a hot rinse is selected for the medicine in use on the health treatment entry page. See picture below:
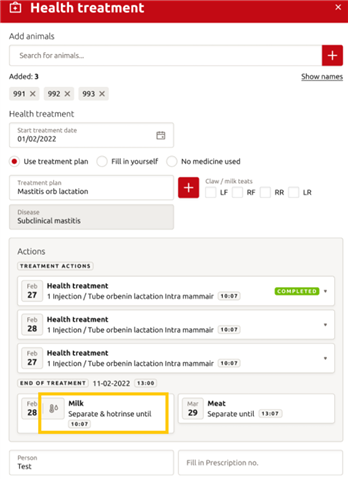
In the milk separation task and reports, there is also a column that shows if a cow/treatment is activated for a hot rinse.
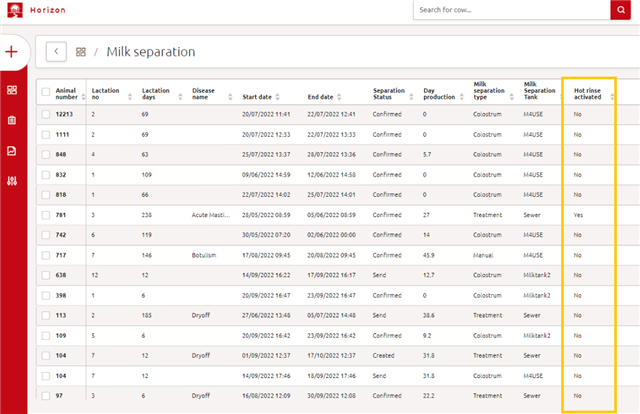
The milk separation entry page mentions that no hot rinse will be done.
In short:
a hot rinse can be enabled or disabled on the medicine settings page (Manage > Health > Medicines). The hot rinse should only be used for oil-based intra-mammary medicines.
A hot rinse is shown on:
The health treatment entryMilk separation modalMilk separation task & report
Attention settings
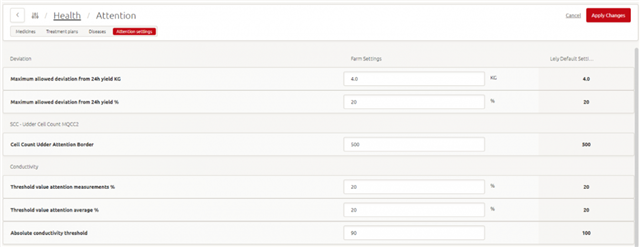
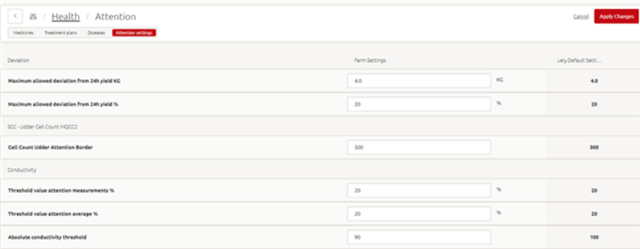
Attentions can be given about udder health, temperature or weight based on the settings. You can change the default settings and adjust the timings until attentions are given in the Attention settings page. The attention settings can be changed for the following parameters:
Where can you find it?
Go to Manage > Attention settings which is part of the Health box
Based on the attention settings, attentions can be given about udder health, temperature or weight. Via the Attention settings page you can change the default settings and having influence on how quick or late attentions are given. For the following parameters, the attention settings can be changed:
Deviation
- Maximum allowed deviation from 24h yield KG. An attention will be generated when the deviation from the 24-hour yield is more than the set number.
- Maximum allowed deviation from 24h yield %. An attention will be generated when the deviation from the 24-hour yield is more than the set percentage.
SCC – Udder Cell Count MQCC2
- Cell Count Udder Attention Border. An attention will be generated when the measured SCC is higher than the set number.
Conductivity
- Threshold value attention measurements %. An attention will be generated when the difference between highest and lowest quarter is higher than the set percentage.
- Threshold value attention average %. An attention is generated when the difference in the average conductivity of the last 3 milkings between the highest and lowest quarter is higher than the set percentage.
- Absolute conductivity threshold. An attention is generated when the conductivity is higher than the set number or higher.
Udder health
- Show manual milk separation. When enabled, cows will appear on report 12 when a manual milk separation is set.
- Show all cows with milk day production drop bigger than x KG. An attention is generated when the day production of a cow is dropped with the set amount or more.
Temperature
- Deviation factor (temperature) %. An attention is generated when a cow has two temperature deviations during the last 5 milkings if the deviation is larger than the set percentage.
Milk Sampling
- Minimum no. of samples. An attention is generated when a cow has not reached the minimum set number of samples during a milk sampling period.
Dry off treatment analysis
A cow’s dry period is an important element in having a successful next lactation, and selecting the most suitable dry off treatment is part of this. Additionally, many farmers are dealing with minimising the use of antibiotics these days (e.g. by decreasing preventative antibiotic usage). Drying off a cow is when antibiotics are often used. To keep cows healthy, it is important to know the effect of a treatment on the health of the cow. For these reasons, we have developed the dry off treatment analysis. On this page, you can analyse the dry off treatments in Horizon and their effectiveness. This will give you the opportunity to optimise your dry off strategy.
Dry off treatment analysis has been developed to analyse the effect of dry off treatments in the herd over time. The results shown in this tool can be used to optimise and fine tune dry off treatments in the future based on their monitored effectiveness.
Where to find the dry off treatment analysis page:
Reports > Health (tab) > Dry off treatment analysis (top right-hand corner)

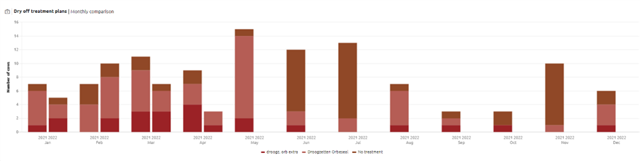
Dry off treatments I Monthly comparison
The dry off treatments bar chart shows the usage of the dry off treatments registered in Horizon for each month. It shows the data for the previous year and the months of the current year until the current date.
Dry off treatment effectiveness last 365 days
The dry off treatment effectiveness last 365 days table provides an overview of the effectiveness of the registered treatments on SCC per lactation number. A tooltip with explanation about the column will appear when you hover over a column header.
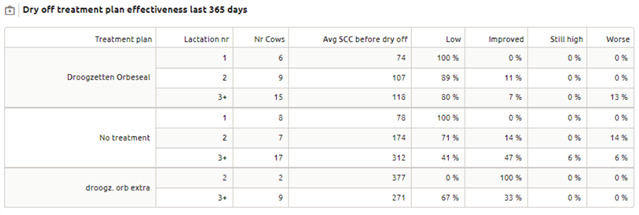
Meaning of the columns:
Lactation nr.: The cows are grouped in lactation 1, 2, and 3 and higher
Avg SCC before dry off: Average SCC 60 days before dry off
Low: SCC before dry off and after calving lower than 250
Improved: SCC before dry off higher than 250 and after calving lower than 250
Still high: SCC before dry off and after calving higher than 250
Worse: SCC before dry off lower than 250 and after calving higher than 250
The time after calving taken into account for calculating the new average cell count for the beginning of the lactation is 35 days.
Cell count measurement (MQCC) or milk sampling data is required to show the dry off treatment analyses. If both are available, the average of the MQCC and the milk sampling are calculated.
Currently, we use the threshold cell count of 250 because this cut-off point is most often used for evaluating the somatic cell count.
